Prickly lettuce (Lactuca serriola) might look like an ordinary roadside weed, but don’t let its unassuming appearance fool you. This wild leafy green has been valued for centuries in traditional medicine, offering surprising health benefits—from supporting kidney function to acting as a natural sedative. Let’s dive into the many advantages of this powerhouse plant and how you can incorporate it into your wellness routine.
1. What is Prickly Lettuce?
Origins and Identification
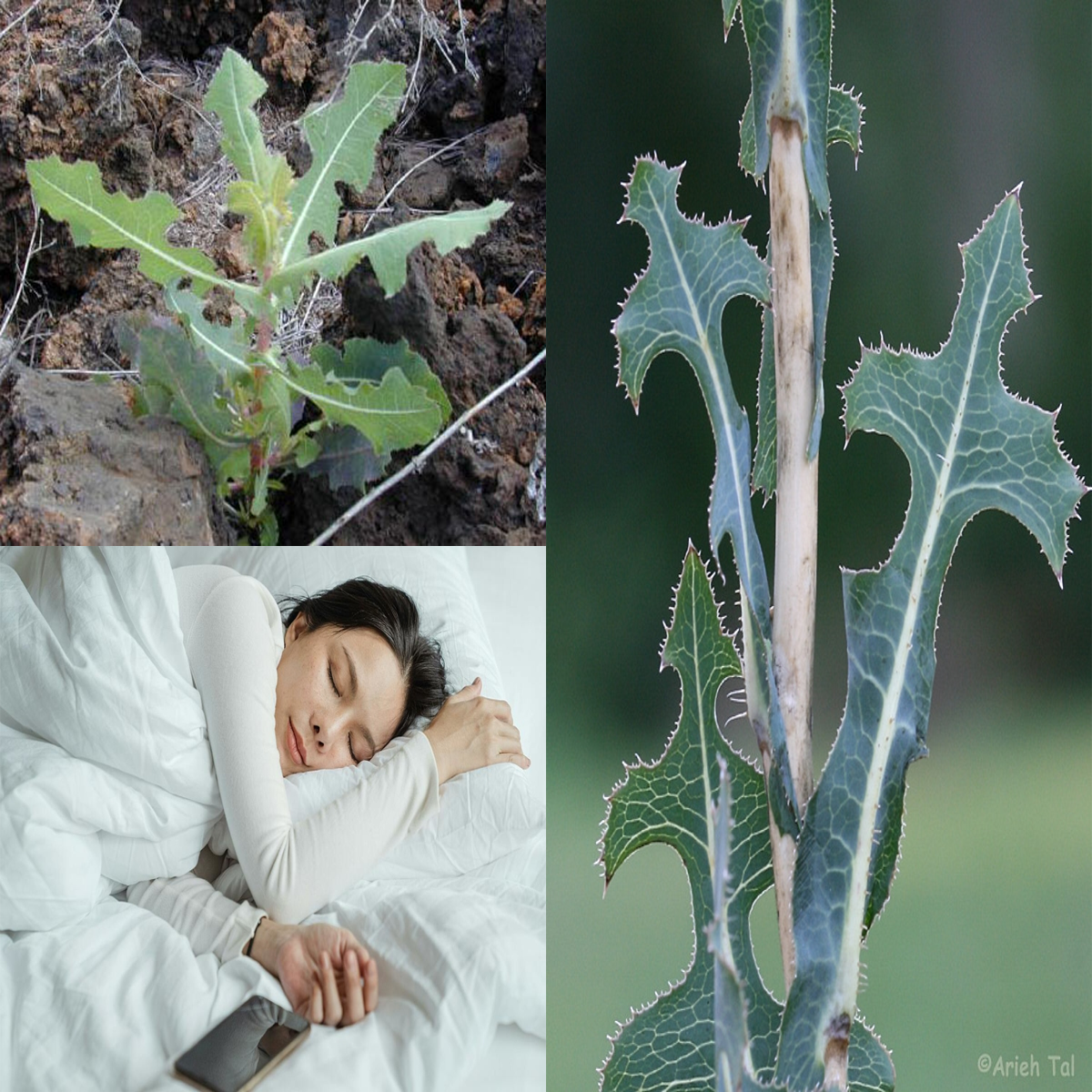
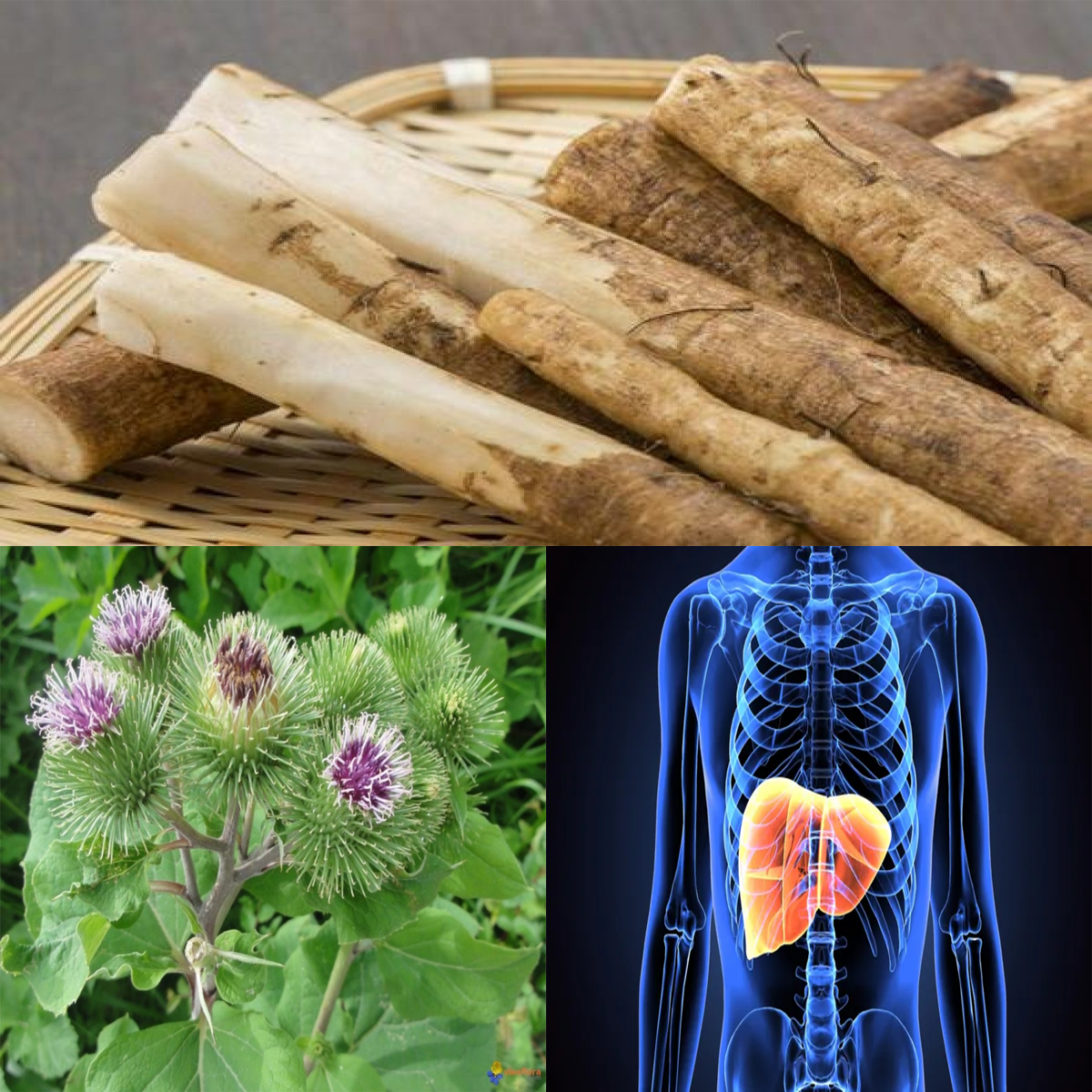
Native to Europe, Asia, and the Mediterranean, prickly lettuce has now spread worldwide, thriving in urban spaces like roadsides and vacant lots. It’s easily recognizable by its tall, spiny stem, bluish-green jagged leaves, and clusters of small yellow flowers. Growing up to 5 feet tall, it’s one of nature’s resilient survivors, flourishing even in poor soil conditions.
A Brief History of Its Use
Ancient civilizations, including the Egyptians and Greeks, valued prickly lettuce for its calming effects. Its milky sap, known as lactucarium, was traditionally used as a natural remedy for pain, insomnia, and anxiety. Because of its mild sedative properties, it even earned the nickname “lettuce opium”—offering relaxation without the risks of addiction.
2. Medicinal and Nutritional Benefits
Lactucarium: A Natural Sedative
One of the most intriguing aspects of prickly lettuce is lactucarium, a milky substance rich in lactucin and lactucopicrin—compounds known for their calming effects. These natural relaxants can help ease anxiety, promote restful sleep, and even offer mild pain relief, making prickly lettuce a great alternative to synthetic sedatives.
Nutritional Powerhouse
Prickly lettuce isn’t just medicinal—it’s also packed with essential nutrients. It contains:
- Vitamin A (for eye health and immunity)
- Vitamin K (for bone strength and blood clotting)
- Iron (for oxygen transport and energy levels)
The young leaves, in particular, are highly nutritious and can be a great addition to a healthy diet.
Antioxidant Properties
Loaded with antioxidants, prickly lettuce helps combat oxidative stress, reducing the risk of chronic illnesses like heart disease, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s. By neutralizing harmful free radicals, this plant supports overall health and longevity.
3. How to Harvest Prickly Lettuce
To get the best out of prickly lettuce, harvest it early when the leaves are tender and less bitter. As the plant matures, the leaves become tougher and more astringent. If collecting for medicinal use, you can extract the sap by making small cuts in the stem. However, always ensure proper identification to avoid toxic lookalikes.
4. How to Use Prickly Lettuce
Medicinal Uses
Traditionally, prickly lettuce has been used to treat anxiety, insomnia, and general stress. Some common ways to use it include:
- Tea: Steep fresh or dried leaves in hot water for a soothing drink before bed.
- Tincture: Extract the active compounds in alcohol for a more concentrated remedy.
- Poultices: Apply crushed leaves to the skin to help with minor aches and pains.
Culinary Uses
While not as popular as cultivated lettuce, young prickly lettuce leaves can be eaten raw in salads, offering a slightly bitter but refreshing flavor. The stems can also be cooked like other leafy greens—stir-fried, boiled, or added to soups.
Precautions
Although generally safe, proper identification is crucial. Some plants resemble prickly lettuce but are toxic. If using it medicinally, consult a healthcare professional—especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medication. Those allergic to lettuce should also avoid it.
5. Preparing and Preserving Prickly Lettuce
Making a Tincture
Tinctures are a great way to preserve and concentrate the medicinal properties of prickly lettuce. Here’s how:
- Blend fresh leaves with high-proof alcohol.
- Let the mixture steep for several days.
- Strain and store in an airtight container.
Drying for Long-Term Use
Drying prickly lettuce preserves its benefits for future use. Using a dehydrator ensures maximum potency, and dried leaves can be stored for months, ready for teas or tinctures.
6. Extracting the Active Compounds
Alcohol Extraction
For a potent medicinal extract, dried prickly lettuce leaves can be steeped in alcohol. A mild heating process enhances the release of lactucarium, making the tincture stronger.
Water Extraction
While alcohol is the most effective solvent, water can also be used to extract beneficial compounds. Combining both methods creates a more comprehensive remedy.
Refining and Storing the Extract
Once extracted, the solution can be further concentrated by evaporating excess liquid. Store the final product in a cool, dark place to maintain its potency.
7. Dosage and Usage Guidelines
Storing the Extract
For maximum effectiveness, keep the tincture in an airtight container in the refrigerator or freezer. Properly stored, it can last for months without losing potency.
Recommended Dosage
For relaxation or sleep support, start with 2-3 dropperfuls of the tincture mixed with water in the evening. Adjust as needed, but always consult a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Final Thoughts
Prickly lettuce is a hidden gem in the world of natural medicine. With its sedative properties, rich nutritional profile, and antioxidant benefits, this overlooked plant deserves a place in your wellness routine. Whether you’re seeking stress relief, better sleep, or a nutritious addition to your diet, prickly lettuce is worth considering. Just remember to harvest responsibly, use it correctly, and enjoy the remarkable benefits of this wild superfood.